1987年5月出生,江苏徐州人,副研究员,硕士生导师。2009年毕业于华中科技大学应用化学专业,2016年在同济大学环境科学与工程学院获得工学博士学位。随后在同济大学环境科学与工程学院从事两年博士后研究工作。2018年入职暨南大学环境学院。
专业研究领域为环境毒理学和生态风险评价,主要研究方向为环境浓度污染物的细菌耐药性突变诱导效应、污染物及降解产物的生物效应和风险评价以及微纳塑料与有机物的联合生物效应和机制。
主要学术贡献和重要研究成果包括:
1.构建以分子模拟技术为基础的污染物联合毒性预测模型,为混合污染物的毒性预测提供新的思路。相关研究成果发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials, Environmental Research等国际期刊上。此外,基于毒物兴奋效应的作用机制,提出了中药用量中剂量效应关系的科学性解释。相关成果发表在Pharmacology & Therapeutics上,并受到广泛的关注。
2.阐述了纳米金属氧化物的毒性机制,揭示了溶出离子在纳米材料毒性作用中的贡献。相关研究成果发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials, Aquatic toxicology等国际期刊上,其中发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials的文章被ESI高被引论文收录。
3.解析了底栖动物沙蚕的肠道微生物结构,并揭示了肠道微生物对污染物在环境中迁移转化的影响。相关研究成果近期发表在Environmental Science & Technology上。
主持和参与的科研项目包括:
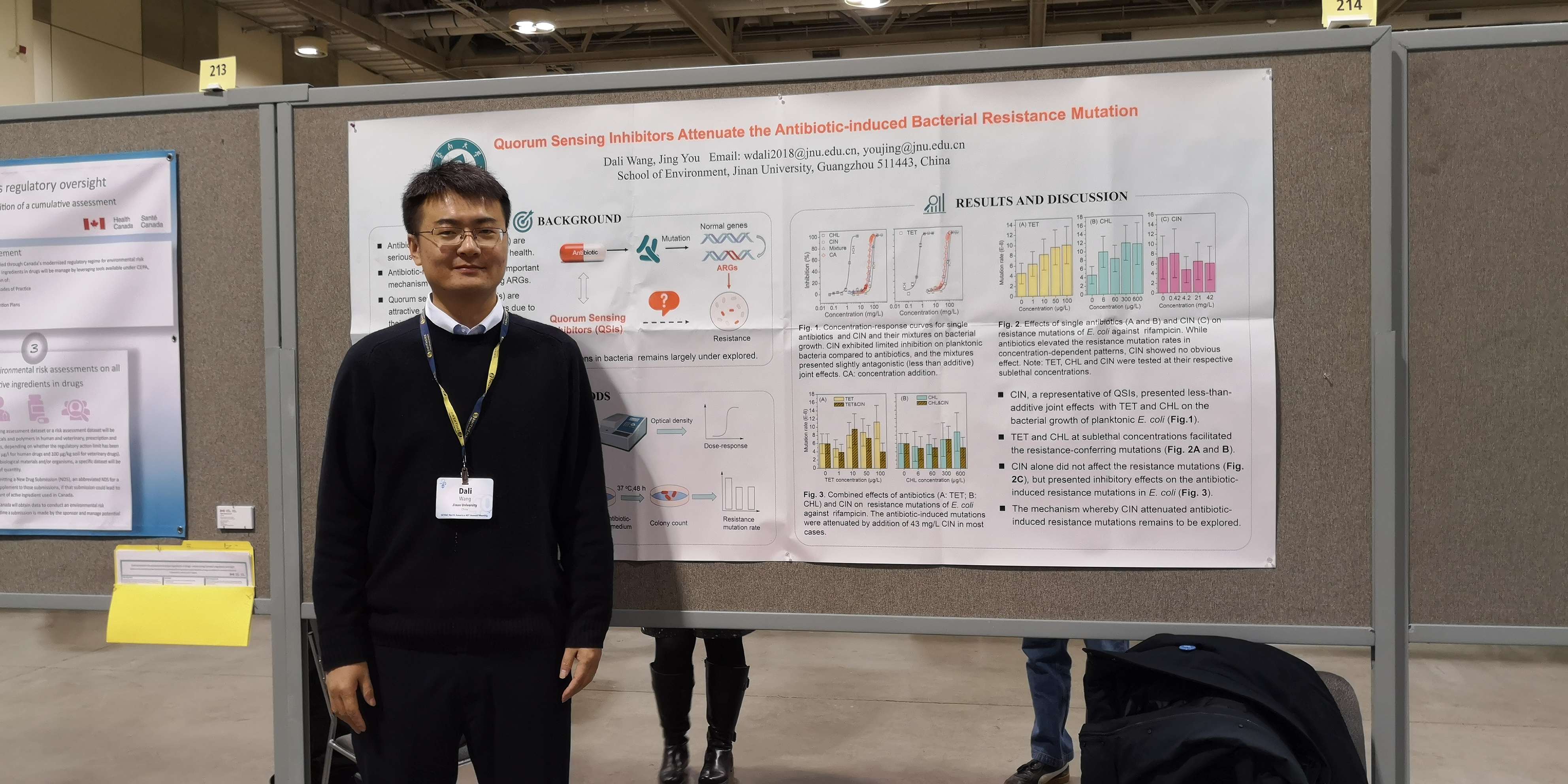
1.国 家自然科学基金青年项目,环境浓度抗生素和纳米抗菌剂对生物膜和细菌抗药性的联合作用与机制,25万元,2019/01-2021/12,在研,主持。
2.广东省自然科学基金-面上项目,群体感应抑制剂对细菌抗性突变的阻遏效应和机制研究,10 万元,2019/10-2022/9,在研,主持
3.国 家自然科学基金重点项目,微纳塑料与典型有机物的复合污染特征及对小动物的生物效应,290万元,2020/1-2024/12,在研,参与
4.NSFC-广东省联合基金,大湾区河口典型有机污染特征及基于多证据链的生态效应,257万,2020/1-2023/12,在研,参与
5.广东省土壤与地下水污染防控及修复重点实验室开放基金,环境浓度抗生素对土壤微生物的生物膜及抗性基因产生和传播的影响,8万元,2019/1-2019/12,已结题,主持
6.中国博士后科学基金(一等)面上项目,磺胺和QSIs对大肠杆菌的联合毒性和耐药性突变影响研究,8万元,2016-2018,已结题,主持
7.上海市化学品分析、风险评估与控制重点实验室开放课题,抗生素和群体感应抑制剂联合暴露对细菌毒性和耐药性影响研究,2万元,2017/1-2018/12,已结题,主持
代表性论文:
(1) Ning, Q.; Wang, D.*; You, J. Joint effects of antibiotics and quorum sensing inhibitors on resistance development in bacteria. Environmental Science-Processes & Impacts 2021. doi:10.1039/D1EM00047K
(2) Ning, Q.; Wang, D.*; Cheng, F.; Zhong, Y.; Ding, Q.; You, J. Predicting rifampicin resistance mutations in bacterial RNA polymerase subunit beta based on majority consensus. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 210.
(3) Wei, F.; Wang, D.*; Li, H.; You, J. Joint toxicity of imidacloprid and azoxystrobin to Chironomus dilutus at organism, cell, and gene levels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 233, 105783.
(4) Wang, D.; Ren, J.; Tan, Z.; You, J.* Gut Microbial Profiles in Nereis succinea and Their Contribution to the Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6235-6243.
(5) Wang, D.; Ning, Q.; Dong, J.; Brooks, B. W.; You, J.* Predicting mixture toxicity and antibiotic resistance of fluoroquinolones and their photodegradation products in Escherichia coli. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114275.
(6) Yao, Z.; Wang, D. (co-first author); Wu, X.; Lin, Z.*; Long, X.; Liu, Y. Hormetic mechanism of sulfonamides on Aliivibrio fischeri luminescence based on a bacterial cell-cell communication. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 793-799.
(7) Wang, D.; Calabrese, E. J.; Lian, B.; Lin, Z.*; Calabrese, V. Hormesis as a mechanistic approach to understanding herbal treatments in traditional Chinese medicine. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2018, 184, 42-50.
(8) Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, J.; Lin, Z.*; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, J. A QSAR-based mechanistic study on the combined toxicity of antibiotics and quorum sensing inhibitors against Escherichia coli. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 438-447.
(9) Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Lin, Z.*; Ding, Y. A comparative study on the binary and ternary mixture toxicity of antibiotics towards three bacteria based on QSAR investigation. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 127-134.
(10) Wang, D.; Lin, Z.*; Wang, T.; Ding, X.; Liu, Y. An analogous wood barrel theory to explain the occurrence of hormesis: A case study of sulfonamides and erythromycin on Escherichia coli growth. Plos One 2017, 12, e181321.
(11) Wang, D.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Z.*; Liu, Y. A Mechanism-based QSTR Model for Acute to Chronic Toxicity Extrapolation: A Case Study of Antibiotics on Luminous Bacteria. Sci. Rep 2017, 7.
(12) Wang, D.; Lin, Z.*; Ding, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y. The Comparison of the Combined Toxicity between Gram-negative and Gram-positive Bacteria: a Case Study of Antibiotics and Quorum-sensing Inhibitors. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 54-61.
(13) Wang, D.; Lin, Z.*; Huo, Z.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z.; Cong, Y. Mechanism-based QSAR Models for the Toxicity of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors to Gram-negative and Gram-positive Bacteria. B. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2016, 97, 145-150.
(14) Wang, D.; Lin, Z.*; Wang, T.; Yao, Z.; Qin, M.; Zheng, S.; Lu, W. Where does the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles come from: The nanoparticles, the ions, or a combination of both? J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 328-334.
(15) Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Z.*; Yao, Z.; Zhang, W. The joint effects on Photobacterium phosphoreum of metal oxide nanoparticles and their most likely coexisting chemicals in the environment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 154, 200-206.
(16) Wang, D.; Lin, Z.*; Yao, Z.; Yu, H. Surfactants present complex joint effects on the toxicities of metal oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 70-75.
(17) Chen, C.; Wang, D. (co-first author); Wang, H.; Lin, Z.*; Fang, Z. A SAR-based mechanistic study on the combined toxicities of sulfonamides and quorum sensing inhibitors on Escherichia coli. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2017, 28, 595-608.